Wurster coating, also known as fluid bed microencapsulation, uses a fluidized bed and differential air flow to encapsulate particles, ensuring a consistent movement and uniform coating. It is a preferred method for the coating of particles, spheres, granules, and tablets.
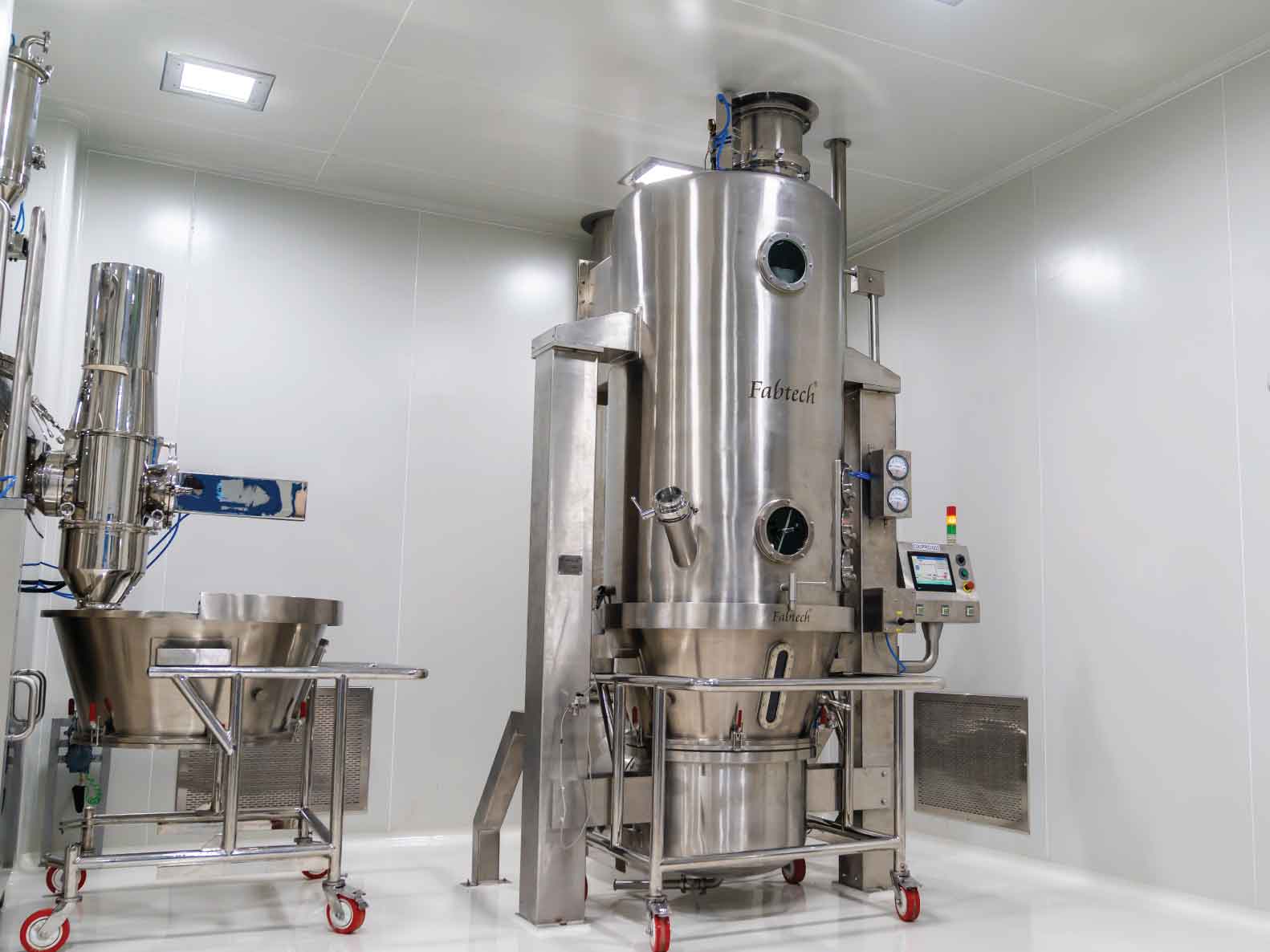

How it Works
In Wurster Fluidized Bed Coating the spray nozzle is beneath the fluidized bed, a unique feature that differentiates our method from conventional coating techniques. It utilizes differential air streams to elevate particles in a cyclical pattern within the chamber, allowing for precise application of atomized coating materials. This strategic configuration guarantees efficient individual particle coating while preventing clumping, achieving a core-shell structure.
Advantages
- Proven to deliver a film coat of unparalleled quality and evenness.
- Optimizes coating thickness, reducing material usage and processing time.
- Adaptable to a diverse array of core materials, particle sizes, and shapes.
- Suitable for small particles, entire capsules, tablets, softgels, extruded materials, powders, crystals, and granules.
No matter the shape—spherical, crystalline, irregular, amorphous—the Wurster process is capable of creating a unique formulation to achieve the desired properties.
Scalability and Flexibility:
- Our expertise extends to scaling the Wurster process from laboratory to commercial production, ensuring consistent formulation and desired drug release profiles.
- We support a broad spectrum of controlled-release pharmaceuticals, offering the versatility to employ both aqueous and solvent-based coating solutions.
Fluid bed Drying vs Spray Drying
Fluidized Bed Spray-Coating:
Application: It’s used to apply a film material evenly onto particles, which can improve shelf life, storage stability, and functionalization of particles.
Process: Particles are fluidized and sprayed with a liquid (solution, suspension, or melt). The liquid evaporates or solidifies, forming a coating layer.
Particle Size: Typically requires particles to be at least 100 micrometers in size for complete coating.
Spray-Drying:
Application: Used to create amorphous, soluble forms of active ingredients, often to overcome solubility challenges of drug candidates.
Process: Involves atomizing a liquid feed into a hot drying medium, which rapidly dries the droplets to form dry particles.
Particle Size: Can handle a range of sizes, typically from 10 to 500 micrometers.
Key Differences:
Feed Characteristics: Spray-drying uses a fluid feed, while fluidized bed processes use solid particles.
Residence Time: Spray-drying has a shorter residence time (seconds to minutes), whereas fluidized bed processes can have longer times (minutes to hours).
Coating vs. Drying:
Fluidized bed spray-coating is primarily used for coating particles, while spray-drying is mainly for drying and particle formation. Both techniques have their specific applications and are chosen based on the desired characteristics of the final product. Fluidized bed spray-coating is more about adding a layer to existing particles, while spray-drying is about creating particles from a liquid feed.
Related Services





FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Spray Drying
Spray drying is a method used to produce a dry powder from a liquid by rapidly drying with a hot gas. This process involves atomizing the liquid into a fine mist and then exposing it to a flow of hot air, causing the solvent to evaporate quickly and leaving behind dry particles. Spray drying is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry to improve the solubility and bioavailability of drugs, create stable powders for formulation, and enable the production of inhalable aerosols.
Spray drying is important in pharmaceuticals for several reasons:
- Enhances Drug Solubility: Many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have poor water solubility, which can be improved through spray drying, enhancing their bioavailability.
- Particle Size Control: It allows precise control over particle size and distribution, critical for consistent drug delivery, especially in inhalation therapies.
- Stability: Spray drying can increase the stability of sensitive compounds by rapidly removing moisture and reducing exposure to heat.
- Formulation Flexibility: Enables the production of various dosage forms, including powders, capsules, and tablets, by incorporating excipients during the drying process.
Spray drying can process a wide range of materials, including solutions, suspensions, and emulsions containing APIs, excipients, and other pharmaceutical ingredients. It is suitable for heat-sensitive compounds due to the rapid evaporation of solvent, minimizing thermal degradation. Spray drying can also handle materials that require specific particle characteristics, such as porosity, density, and surface morphology, for targeted drug delivery applications.
Yes, spray drying can significantly improve the bioavailability of drugs. By converting poorly soluble drugs into amorphous solid dispersions with enhanced dissolution rates, spray drying can increase the rate and extent of drug absorption in the body. This process is particularly beneficial for BCS Class II drugs, which have high permeability but low solubility.
Our spray drying services offer comprehensive capabilities, including:
- Development and optimization of spray drying processes tailored to specific API properties and formulation requirements.
- Scalability from pilot-scale batches for feasibility studies and clinical trials to full-scale commercial production.
- Particle engineering to achieve desired particle size, morphology, and physicochemical properties.
- Encapsulation of volatile or sensitive compounds to enhance stability and control release.
- Analytical support for characterizing spray-dried products, including particle size distribution, moisture content, and thermal properties.
We can handle a broad range of spray drying operations, from small-scale pilot projects for early-stage development and clinical trial materials to large-scale commercial production. Our facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art spray dryers that can be adjusted to accommodate different batch sizes, throughput requirements, and product specifications, ensuring flexibility and scalability to meet our clients' needs.
We ensure the quality of spray-dried products through stringent quality control measures and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). This includes:
- Raw material inspection to verify purity and compliance with specifications.
- Process monitoring and control using advanced instrumentation to maintain optimal drying conditions.
- In-process testing to assess critical quality attributes such as moisture content and particle size.
- Final product testing to confirm compliance with all specifications and regulatory requirements.
- Documentation and traceability of all manufacturing and testing activities.
Yes, spray drying can be used to develop controlled release formulations. By encapsulating the API within a matrix of polymer or other excipients that control the release rate of the drug, spray drying can produce particles that release the drug over a desired time frame. This technique is useful for both immediate-release and sustained-release formulations, offering flexibility in drug delivery strategies.
Our spray drying services comply with all relevant regulatory standards, including those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Medicines Agency (EMA), and International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines for pharmaceutical manufacturing. We ensure that our processes, equipment, and facilities meet the stringent requirements for GMP compliance, ensuring the highest level of quality and safety for all spray-dried products.
We handle heat-sensitive compounds by optimizing the spray drying process to minimize thermal exposure. This can involve adjusting the inlet and outlet temperatures, feed rate, and atomization parameters to ensure rapid solvent evaporation without compromising the integrity of the heat-sensitive compound. Additionally, we can use cryogenic spray drying or employ protective excipients that encapsulate and shield the compound from heat. Our expertise in process development allows us to tailor the drying conditions to the specific thermal sensitivity of each compound, ensuring its stability and activity.