Pharmaceutical tablets are solid dosage forms made by compressing a drug (API) with or without other ingredients. Tablets are popular because they are easy to take, identify, and generally taste better than other forms. They make up about 70% of the market for oral solid dose (OSD) forms. Other OSD forms include powders, granules, and sachets. Tablets are precise in dosing and cost-effective. They contain APIs and excipients like binders, lubricants, and fillers. These ingredients are blended to ensure a uniform mixture.
Despite their wide-use and proven manufacturing pedigree, tablets can still present significant manufacturing challenges. Our diverse tablet forms cater to a wide array of therapeutic needs and patient preferences, ensuring the success of your project. We can navigate the complexities of tablet formulation and manufacturing.

Advanced Tablet Forms
Mono And Bi-Layer Tablets
Mono and bi-layer tablets are pharmaceutical formulations designed to deliver one or more active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with varying release profiles, aimed at enhancing therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance. Mono-layer tablets contain a single layer of medication, providing either an immediate or sustained release of the drug. In contrast, bi-layer tablets are engineered to combine two different APIs or control the release rates of a single API, achieving both immediate and extended drug release within one dosage form. This design is particularly beneficial for medications requiring distinct release phases or for combining APIs that might be chemically or physically incompatible if mixed together directly. For instance, one layer can offer an immediate release for rapid onset of action, while the second layer provides a sustained release to maintain therapeutic levels over an extended period, ensuring comprehensive treatment coverage and improving patient adherence by reducing the pill burden.
Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs)
Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs) integrate multiple APIs into a single dosage form, streamlining medication regimens and significantly enhancing patient adherence, particularly for chronic conditions that necessitate the concurrent use of multiple medications. This simplification is crucial in the management of complex diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis, and hypertension, where patients are often required to take several medications daily. By consolidating these medications into one pill, FDCs reduce the complexity and frequency of dosing, thereby improving treatment outcomes and patient quality of life. Moreover, FDCs help in minimizing the risk of medication errors, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the therapeutic regimen.
Micro And Mini Tablets
Micro and mini tablets are specialized formulations tailored specifically for pediatric and geriatric patients, who often encounter difficulties with standard tablet sizes. These smaller tablets are designed to enhance swallowability and provide precise dosing, making medication administration more manageable and accurate for these sensitive patient groups. Micro tablets, typically measuring less than 2 mm in diameter, and mini tablets, generally between 2 and 4 mm, offer significant advantages in terms of dose flexibility and titration. This is particularly beneficial in pediatric care, where dosing needs to be carefully adjusted according to the child’s age and weight, and in geriatric care, where swallowing difficulties are common. These tablets also facilitate the development of combination therapies and customized dosing regimens, improving overall treatment efficacy and patient compliance.
Aqueous Film Coating
Aqueous film coating is a tablet coating technique that enhances the appearance, swallowability, and stability of tablets. This process involves applying a thin polymer-based film dissolved in water to the tablet surface, providing a protective barrier that shields the API from environmental factors such as moisture and light. Aqueous film coating is preferred over organic solvent-based coatings due to its safety, both for the patient and the environment, as it eliminates the risks associated with residual organic solvents. This coating method not only improves the visual appeal of the tablets but also enhances their mechanical strength, reduces dusting, and can be used to modify the release characteristics of the drug.
Chewable Tablets
Chewable tablets are designed to be chewed and then swallowed, offering an alternative dosage form for patients who have difficulty swallowing traditional tablets. These tablets are typically flavored to improve taste and palatability, making them particularly suitable for pediatric and geriatric patients. The act of chewing helps to break down the tablet, facilitating faster disintegration and absorption of the medication. This dosage form is ideal for delivering medications that benefit from rapid onset of action, as the drug is released and absorbed quickly once ingested. Chewable tablets are commonly used for vitamins, antacids, and certain analgesics, enhancing patient compliance and ensuring effective treatment.
Effervescent Tablets
Effervescent tablets are formulated to dissolve in water, creating a solution that can be easily ingested by patients who have difficulty swallowing solid dosage forms. These tablets contain a mixture of acids and bicarbonates, which react in the presence of water to produce carbon dioxide, leading to effervescence. This reaction helps to disperse the active ingredients uniformly in the water, ensuring consistent dosing and rapid drug absorption. Effervescent tablets are particularly beneficial for medications requiring quick onset of action, such as analgesics, antipyretics, and certain vitamins and supplements. The effervescence also helps to mask the taste of the medication, improving patient compliance.
Customization Options
Our tablets are available in various shapes and sizes, offering multiple customization options to meet specific therapeutic needs and patient preferences. These options include:
• Film-Coating: Enhances the visual appeal of the tablets, improves swallowability, and provides a protective barrier for the API.
• Sugar-Coating: Masks unpleasant tastes, making the tablets more palatable and improving patient compliance, particularly in pediatric and geriatric populations.
• Enteric-Coating: Protects the drug from the acidic environment of the stomach, ensuring that it is released in the intestine where it can be absorbed effectively. This is particularly important for medications that can be degraded by stomach acid or cause gastric irritation.
Disintegration Control
We can precisely control the disintegration time of tablets to match the desired release profile of the medication. By manipulating the tablet formulation and using specific disintegrants, we ensure that the medication is released at the right time and place in the body. This optimization is crucial for achieving the intended therapeutic outcomes, as it allows for the synchronization of drug release with the physiological needs of the patient, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Taste Masking
For APIs with unpleasant tastes, we offer a range of taste-masking solutions to enhance patient compliance. These techniques include coating the API with taste-masking agents, microencapsulation to create a barrier between the API and the taste buds, and the use of flavoring agents to improve the overall taste profile. Effective taste masking is particularly important in pediatric and geriatric populations, where palatability can significantly impact adherence to the medication regimen.
Sustained-Release Formulations
Sustained-release formulations are designed to release the drug slowly over an extended period, maintaining a steady therapeutic level in the bloodstream and reducing the frequency of dosing. This can improve patient compliance and ensure a more consistent therapeutic effect. Technologies used in sustained-release formulations include matrix systems, reservoir systems, and osmotic pumps.
Pulsed-Release Formulations
Pulsed-release formulations release the drug in bursts at specific intervals. This can be beneficial for conditions requiring periodic dosing or targeting specific times of the day. These formulations can be achieved using multi-layer tablets, coated pellets, or pulsatile drug delivery systems.
Modified-Release Formulations
Modified-release formulations are designed to achieve a desired release profile tailored to the therapeutic needs of the patient. This ensures optimal drug absorption and efficacy. These formulations can include extended-release, delayed-release, and targeted-release systems. Techniques such as hot melt extrusion and 3D printing are often used to create these formulations.
Delayed-Release Formulations
Delayed-release formulations prevent the drug from being released until it reaches a specific part of the gastrointestinal tract. This can protect the drug from stomach acid or target drug release to the intestines. Enteric coatings are commonly used to achieve delayed-release, ensuring the drug is released in the desired location.
Orodispersible Tablets (ODTs)
Orodispersible tablets (ODTs) disintegrate rapidly in the mouth without the need for water, improving patient compliance, especially for those with swallowing difficulties. These tablets are designed to dissolve on the tongue, providing a convenient and easy-to-administer dosage form.
Mucoadhesive Tablets
Mucoadhesive tablets adhere to the mucosal lining of the gastrointestinal tract, providing localized drug delivery and prolonged contact time for enhanced absorption. These tablets can be used to target specific areas within the GI tract, improving the bioavailability of the drug and reducing systemic side effects.
Benefits of Tablets
Accurate Dosage: Tablets provide a highly precise and consistent dosage of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), ensuring that patients receive the correct amount of medication with each dose. This precision is crucial for the efficacy and safety of the treatment, as even slight deviations in dosage can significantly impact therapeutic outcomes and patient health. The manufacturing processes for tablets are rigorously controlled, involving precise measurement and mixing of ingredients, which guarantees uniformity in every tablet produced. This consistency is particularly important for medications with narrow therapeutic indices, where the difference between an effective dose and a toxic dose is small.
Stability: Tablets generally exhibit superior stability compared to liquid forms of medication, which contributes to maintaining the drug’s efficacy over extended periods. The solid state of tablets protects the API from degradation caused by environmental factors such as light, air, and moisture. This enhanced stability is achieved through careful selection of excipients and advanced manufacturing techniques that ensure the active ingredients remain potent throughout the tablet’s shelf life. Additionally, many tablets are coated with protective layers that further shield the API from external elements, enhancing the overall stability and longevity of the medication.
Cost-Effective: The production of tablets is relatively inexpensive compared to other dosage forms, making them a cost-effective option for both pharmaceutical manufacturers and consumers. The cost-effectiveness of tablets is due to several factors, including the efficiency of the manufacturing process, the relatively low cost of raw materials, and the scalability of production. Tablets can be produced in large batches using automated machinery, which reduces labor costs and increases production speed. The affordability of tablets makes them accessible to a broader population, contributing to better health outcomes by ensuring that essential medications are within reach of those who need them.
Ease of Use: Tablets are designed for ease of handling, storage, and transport, making them highly convenient for both healthcare providers and patients. Their compact and solid form allows for straightforward packaging, which can be tailored to various distribution needs, including blister packs and bottles. For patients, tablets offer the convenience of simple administration, with many formulations available that cater to different preferences, such as chewable tablets for those who have difficulty swallowing or dissolvable tablets for rapid onset of action. The ease of use associated with tablets enhances patient adherence to medication regimens, leading to more effective treatment outcomes.
Taste Masking: One of the significant advantages of tablets is their ability to mask the unpleasant taste of certain APIs, thereby improving patient compliance. Many APIs have bitter or otherwise unpalatable tastes that can deter patients from adhering to their prescribed treatments. Tablets can be formulated with taste-masking agents or coated with flavor-neutralizing layers that prevent the API’s taste from being perceived by the patient. This feature is particularly beneficial for pediatric and geriatric populations, who may be more sensitive to unpleasant tastes and therefore more likely to skip doses if the medication is unpalatable.
Versatility: Tablets are highly versatile and can be formulated in various ways to control the release of the drug, catering to different therapeutic needs. Immediate-release tablets provide rapid onset of action, while extended-release formulations ensure a sustained release of the medication over time, reducing the frequency of dosing and enhancing patient compliance. Enteric-coated tablets are designed to pass through the stomach and dissolve in the intestines, protecting the API from stomach acid and minimizing gastric irritation. This versatility allows for the customization of tablets to meet specific therapeutic goals and patient preferences.
Identification: Tablets can be easily identified by their distinctive shape, size, color, and markings, which significantly reduces the risk of medication errors. The unique physical characteristics of tablets, often embossed or imprinted with specific codes or logos, help healthcare providers, pharmacists, and patients quickly and accurately identify the correct medication. This ease of identification is crucial in preventing dispensing errors, ensuring that patients receive the right medication at the right dose. The use of different colors and shapes also aids in distinguishing between various medications, further enhancing safety in medication management.
Patient Compliance: The convenience and ease of taking tablets contribute significantly to better patient adherence to prescribed treatment regimens. Tablets are simple to administer, requiring no special preparation or equipment, which makes them an attractive option for patients of all ages. The availability of various tablet formulations, such as those designed for once-daily dosing or chewable forms, addresses individual patient needs and preferences, further promoting adherence. Improved patient compliance leads to more consistent therapeutic effects, reducing the likelihood of treatment failures and enhancing overall health outcomes.
Long Shelf Life: Tablets typically have a longer shelf life compared to other dosage forms, such as liquids or suspensions, which helps in reducing waste and ensuring the availability of the medication. The solid state of tablets makes them less susceptible to degradation over time, allowing them to retain their potency and efficacy for extended periods. This long shelf life is particularly advantageous for medications that are stored in less-than-ideal conditions, such as those distributed in regions with limited access to climate-controlled storage facilities. By maintaining their stability over time, tablets help ensure that patients receive effective treatment even in challenging environments.
Protection of API: Tablets offer significant protection for unstable drug substances from environmental factors like light, moisture, and air, enhancing the stability and shelf life of the medication. Many APIs are sensitive to these elements, which can lead to degradation and reduced efficacy if not properly protected. Tablets can be formulated with protective coatings and excipients that shield the API from environmental exposure, preserving its therapeutic integrity. This protection is critical for ensuring that patients receive medications that are both safe and effective throughout the entire shelf life of the product.
Controlled Release: Tablets can be designed to release the drug at a specific rate, providing sustained therapeutic effects and reducing the frequency of dosing. Controlled-release formulations, such as extended-release or delayed-release tablets, are engineered to release the API gradually over time, maintaining a consistent drug concentration in the bloodstream. This controlled release minimizes the peaks and troughs associated with immediate-release formulations, reducing the risk of side effects and enhancing the overall effectiveness of the treatment. By optimizing the release profile of the drug, controlled-release tablets improve patient outcomes and adherence.
Reduced Risk of Contamination: Tablets are less prone to contamination compared to liquid forms, as they are typically sealed in blister packs or bottles that protect them from external contaminants. The solid state of tablets and their packaging provide a robust barrier against microbial contamination, reducing the risk of infections or other adverse effects associated with contaminated medications. The manufacturing process for tablets also involves stringent quality control measures to ensure that each batch meets high standards of purity and safety. This reduced risk of contamination makes tablets a reliable and safe option for medication delivery.
Ease of Manufacturing: The manufacturing process for tablets is well-established and can be easily scaled up, making it suitable for large-scale production. The production of tablets involves a series of standardized steps, including granulation, compression, and coating, which can be efficiently managed using automated equipment. This scalability allows pharmaceutical companies to meet high demand and ensure a consistent supply of medications. The streamlined manufacturing process also enables cost-effective production, contributing to the affordability of tablets for consumers. The ease of manufacturing tablets ensures that essential medications can be produced and distributed widely, supporting public health initiatives.
Customizable: Tablets can be customized in terms of size, shape, and color, which can help in branding and patient recognition. Pharmaceutical companies can design tablets with specific characteristics that align with their brand identity, making them easily recognizable to consumers. This customization can also aid in patient adherence by making medications more visually appealing and easier to identify. For example, different colors can be used to differentiate between various dosages of the same medication, reducing the risk of dosing errors. The ability to customize tablets enhances their utility and appeal, benefiting both manufacturers and patients.
Reduced Side Effects: By controlling the release of the drug, tablets can minimize the risk of side effects associated with peak concentrations of the medication in the bloodstream. Extended-release formulations are designed to maintain a steady drug concentration, avoiding the sharp spikes that can occur with immediate-release tablets. These spikes can lead to side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort or cardiovascular issues. Controlled-release tablets provide a more gradual absorption of the drug, improving tolerability and patient comfort. This reduction in side effects contributes to better patient adherence and more successful treatment outcomes.
HPAPI Tablets
HPAPIs in Tablets: Highly Potent Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (HPAPIs) are notable for their high potency and effectiveness at very low doses, typically at or below 150 micrograms per kilogram of body weight in humans. This remarkable potency makes them especially suitable for incorporation into oral solid dosage forms such as tablets, which offer patients not only ease of administration but also precise and consistent dosing. HPAPIs are of particular importance in the development of cancer therapeutics, with approximately 60% of approved oncology treatments relying on these potent compounds. This prevalence underscores the critical role of HPAPIs in modern pharmaceutical formulations, enabling effective treatment options for patients with serious and life-threatening conditions.
Handling and Safety Measures: In our Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO), we prioritize the safety of our workers and the environment through the implementation of robust containment strategies specifically designed to handle HPAPIs. These strategies include the use of isolators, which are specialized enclosures that allow manipulation of HPAPIs within a sealed environment, and contained transfer systems that prevent the release of these potent compounds during processing. Our dedication to safety extends to the utilization of dedicated equipment for the handling of HPAPIs, which significantly minimizes the risk of cross-contamination and ensures the purity and quality of the final tablet products. These measures are essential to maintaining a safe working environment and protecting the integrity of our pharmaceutical products.
Formulation Challenges: One of the primary formulation challenges associated with HPAPIs in tablet form is their often poor solubility and bioavailability, which can impede drug absorption and effectiveness. To address these issues, we employ specialized techniques such as particle size reduction, which increases the surface area of the HPAPI particles and enhances their dissolution rate. Additionally, we use solid dispersion technology, which involves dispersing the HPAPI in a carrier matrix to improve its solubility and bioavailability. Ensuring uniform dosing is another critical aspect of HPAPI formulation, particularly given the low concentrations at which these potent compounds are effective. Our precision manufacturing processes are designed to achieve consistent distribution of HPAPIs within each tablet, thereby guaranteeing that each dose delivers the intended therapeutic effect.
Manufacturing Considerations: The chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) associated with HPAPIs present unique challenges due to the stringent containment and control measures required to safely handle these potent compounds. Our production processes for HPAPIs are characterized by a high degree of precision and control, which is essential given the small quantities of the drug involved and the necessity for accurate dosing in the final tablet form. We implement rigorous containment and control measures throughout the manufacturing process to ensure both safety and efficacy. This includes the use of advanced technologies and practices designed to prevent contamination and ensure the consistent quality of the tablets produced. Our commitment to meticulous manufacturing practices is crucial to delivering safe, effective, and reliable HPAPI-based medications to patients.
Additional Benefits
Flexible Manufacturing Solutions for Tablets: We offer a comprehensive array of flexible manufacturing solutions, adept at handling a wide spectrum of tablets, ranging from routine to high-potency and complex forms. Our state-of-the-art facilities are meticulously designed to accommodate an extensive variety of tablet types, including coated tablets, which are engineered to mask taste or improve stability; matrix tablets, which utilize a polymer matrix for controlled drug release; bi-layered tablets, which enable the combination of two distinct drugs or release profiles; and mini-tablets, which are smaller in size for ease of swallowing and precision dosing. Each manufacturing process is optimized to ensure consistency, quality, and efficiency, employing the latest technological advancements to meet the diverse needs of the pharmaceutical industry.
Packaging, Labeling, and Serialization of Tablets: Our company provides comprehensive end-to-end solutions for the packaging, labeling, and serialization of tablets, addressing both clinical and commercial manufacturing needs. We cater to various packaging formats, including blister packs, bottles, and cartons, each designed to ensure product safety and integrity. Our advanced labeling systems are capable of handling complex labeling requirements, ensuring clarity, compliance, and traceability. Furthermore, our serialization services are designed to comply with global regulatory requirements, utilizing cutting-edge technology to assign unique identifiers to each package. This ensures robust tracking and tracing capabilities, which are essential for combating counterfeit drugs and ensuring patient safety.
Quality Control and Analytical Development for Tablets: Our facilities are equipped with cutting-edge quality control. Alongside our preformulation and analytical development infrastructure, we conduct rigorous testing and validation processes to ensure that every tablet meets stringent safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Our quality control processes include in-depth chemical, physical, and microbiological testing, employing advanced analytical techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and mass spectrometry (MS). This ensures that each batch of tablets is consistent, safe, and effective.
Research and Development for Tablets: Our research and development (R&D) pilot lab is at the forefront of pioneering the next generation of tablet formulations. We work in close collaboration with our partners to develop innovative tablet formulations that address specific therapeutic needs and market demands. Our R&D team employs a multidisciplinary approach, integrating expertise in pharmaceutical sciences, materials science, and engineering to develop novel drug delivery systems and formulations. This collaborative approach enables us to accelerate the development process, bringing new and effective tablet products to market more efficiently.
Temperature-Controlled Warehousing for Tablets: To preserve the integrity and quality of your tablet products, we offer temperature-controlled warehousing solutions. Our warehousing facilities are designed to maintain optimal storage conditions, including controlled temperature and humidity levels, to ensure that your tablets remain stable and effective throughout the supply chain. We employ advanced monitoring systems to continuously track storage conditions, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards. This comprehensive approach to warehousing ensures that your products are protected from environmental factors that could compromise their quality, ultimately ensuring that patients receive safe and effective medications.
Steps Involved in Drug Product Development of Tablets
Preformulation Studies: Before the actual formulation process begins, it is crucial to conduct extensive preformulation studies, which involve a thorough analysis of the drug’s physical and chemical properties to guide the formulation design. These studies encompass several key aspects:
- Solubility: Determine the solubility of the drug in various solvents, which is essential for understanding how the drug will dissolve and be absorbed in the body. Solubility studies help in selecting appropriate solvents and formulation strategies to enhance bioavailability.
- Stability: Evaluate the stability of the drug under different environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. Stability studies ensure that the drug maintains its efficacy, safety, and shelf-life over time.
- Compatibility: Investigate the compatibility of the drug with other excipients (inactive ingredients) that will be used in the formulation. This step is vital to ensure that no adverse reactions occur between the drug and other ingredients, which could affect the drug’s effectiveness or cause undesirable side effects.
Dispensing: Accurately weigh and measure all ingredients, including the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients, to ensure the correct amounts are used in the formulation. Precision in this step is crucial to maintain consistency and uniformity in the final product. The accuracy of dispensing affects the dosage strength and overall quality of the tablets.
Sizing: Reduce the size of the ingredients into fine particles through milling or grinding processes to improve their flow and mixing properties. Sizing helps achieve a uniform particle size distribution, which is essential for consistent blending and optimal tablet compression. Smaller particles enhance the dissolution rate and bioavailability of the drug.
Powder Blending: Thoroughly mix the ingredients to ensure that each tablet contains the correct amount of the API and excipients. Homogeneous blending is critical to avoid dosage variations and ensure that each tablet meets the specified quality standards. This step involves using mixers or blenders designed to achieve uniform distribution of all components.
Granulation: Form granules from the powder mixture to improve flow properties and processing efficiency. Granulation can be performed using either dry or wet methods:
- Dry Granulation: Compress the powder mixture into large, compact pieces, which are then broken down into granules. This method is suitable for moisture-sensitive drugs.
- Wet Granulation: Add a granulating liquid to the powder mixture to form a wet mass, which is then dried and screened into granules. Wet granulation enhances the cohesiveness and compressibility of the mixture, making it easier to handle during tablet compression.
Drying & Dry Screening: After granulation, dry the granules to remove any residual moisture, which can affect the stability and compressibility of the final product. Once dried, pass the granules through a screen to achieve the desired size distribution. This step ensures uniformity and improves the flow properties of the granules.
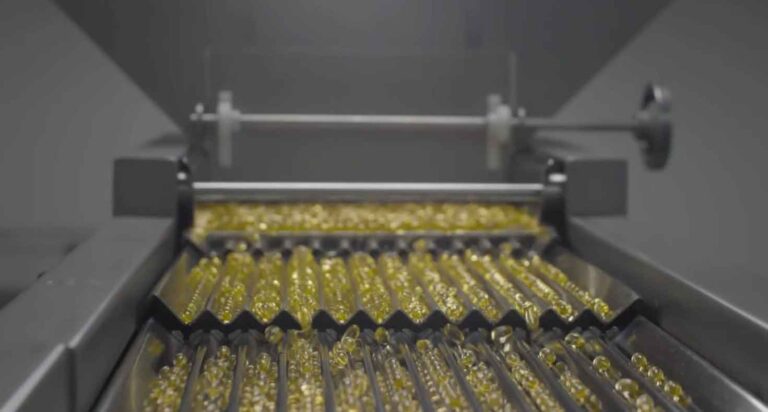
Tablet Compression: Compress the dried powder or granule mixture into tablets using a tablet press machine. This step involves applying pressure to form the tablets, ensuring they are compact and have the required mechanical strength. The compression process must be carefully controlled to produce tablets with consistent weight, hardness, and disintegration time.
Coating: Apply various types of coatings to the tablets for multiple purposes, including:
- Masking Unpleasant Tastes: Coatings can cover the bitter or unpleasant taste of the API, improving patient compliance.
- Modifying Release Profiles: Functional coatings can control the release rate of the API, allowing for immediate, delayed, or extended release of the drug.
- Protecting the Tablet: Coatings provide a protective barrier against environmental factors such as moisture, light, and air, enhancing the stability and shelf-life of the tablets.
Services





FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Oral Solids
Oral solid dosage forms include tablets, capsules, powders, and granules. They are the most popular method of drug delivery due to their convenience, stability, and ease of mass production. These forms allow for precise dosages, extended shelf life, and improved patient compliance, making them a staple in both over-the-counter and prescription medication markets.
We offer comprehensive services for oral solid dosage forms, including formulation development, process optimization, scale-up, and manufacturing. Our capabilities extend to immediate and controlled-release formulations, coating, encapsulation, and the development of chewable, dispersible, and effervescent tablets. We also provide packaging and analytical testing services to ensure product quality and compliance.
Quality and compliance are paramount in our operations. We adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and are regularly inspected by regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA. Our quality control processes include rigorous testing of raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products. We also implement robust quality assurance protocols, including validation and stability studies, to ensure our products meet all regulatory standards.
Yes, we have specialized facilities and containment systems designed to safely handle controlled substances. Our team is experienced in managing the unique challenges associated with these substances, including stringent regulatory requirements and the need for specialized equipment and safety protocols.
Our production capacity is flexible and scalable to meet the needs of our clients, ranging from small-scale batch production for clinical trials to large-scale manufacturing for commercial supply. Our facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art machinery for granulation, compression, and coating, allowing us to efficiently produce a wide range of batch sizes with high precision and consistency.
For generic products, we focus on bioequivalence studies, cost-effective formulation, and process optimization to ensure competitive market entry. For novel oral solid dosage forms, we collaborate closely with our clients to develop innovative formulations that enhance bioavailability, improve patient compliance, and extend product lifecycle, leveraging our expertise in drug delivery technologies and formulation science.
Our formulation development and optimization process is data-driven and collaborative. We utilize Quality by Design (QbD) principles, incorporating thorough understanding of the drug substance, target product profile, and manufacturing processes. We employ advanced modeling and simulation tools, along with high-throughput screening methods, to rapidly identify and optimize formulations that meet the desired product attributes.
Project management is a core competency of our operations. We assign dedicated project managers to each client, who oversee all aspects of the project from inception to delivery. Our project managers work closely with clients to establish clear timelines, milestones, and communication plans. We utilize agile manufacturing practices and real-time monitoring to ensure projects remain on track and adjustments are made proactively to meet delivery commitments.
While confidentiality agreements restrict the details we can share, we have successfully partnered with numerous pharmaceutical companies to bring both generic and innovative oral solid dosage products to market. Our collaborations often involve overcoming complex formulation challenges, scaling up novel production processes, and navigating regulatory approvals efficiently.
Starting a project with us is straightforward. Interested pharmaceutical companies can contact us through our website, email, or phone to schedule an initial consultation. During this consultation, we discuss the project scope, objectives, and timelines. Following this, we provide a proposal outlining our services, timelines, and cost estimates. Upon agreement, we initiate the project with a kick-off meeting to align on project details and establish communication protocols.