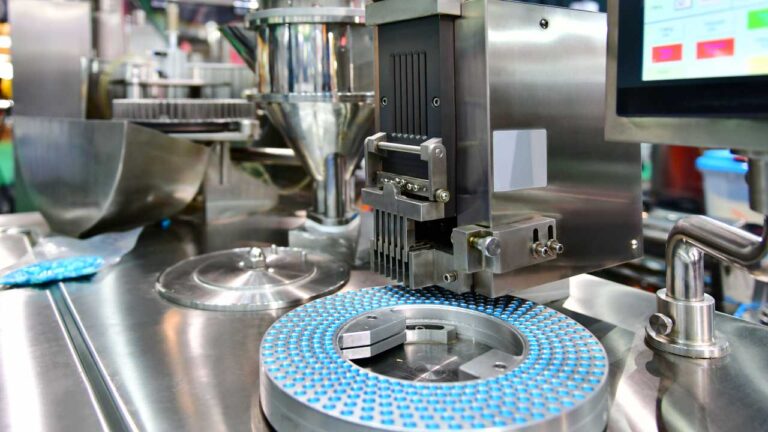
Oral solid dosage (OSD) forms account for the majority of pharmaceutical therapies. Today, OSD forms such as small molecules, tablets, capsules, soft gels, effervescence, gummies, and pills are the most common dose form physicians prescribe for a variety of indications. They are ingested orally, dissolve in the digestive system, and deliver the active ingredients into the bloodstream through absorption. Despite their wide-use and proven manufacturing pedigree, OSDs can still present significant challenges. With an increase in complex molecules, it is critical to provide diverse formulation and oral solid solutions. We deliver a wide range of oral solid dosage forms:
- Tablets (mono and bi-layer) – immediate and modified release delivery systems
- Fixed-dose combinations (FDCs)
- Micro and Mini tablets
- Aqueous film coated tablets
- Capsules
- Beads, including multi-particulate fluid bead coating
- Granules for reconstitution
- Powders including powder-in-bottle (PiB) dosage forms
- Stick packs
Oral Solid Forms Offered
- Oral Solids and Bi-layer Tablets: Our oral solids portfolio includes bi-layer tablets, which allow for the combination of two Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or distinct release profiles, offering a versatile solution for combination therapies.
- Oral Solids and Fixed-Dose Combinations (FDCs): The oral solids form of FDCs simplifies medication regimens by combining multiple APIs into a single dosage, thereby enhancing patient adherence and simplifying treatment protocols.
- Micro and Mini Tablets: Tailored for pediatric and geriatric patients, our oral solids range features micro and mini tablets, making dosing more manageable and precise for these sensitive patient groups.
- Aqueous Film Coating: Our oral solids’ aqueous film coating process not only enhances the appearance and swallowability of tablets but also provides a protective barrier for the API, ensuring drug stability and efficacy.
- Multi-particulate Bead Coating: Oral solids benefit from our multi-particulate bead coating, which ensures a uniform coating for multiparticulate systems, guaranteeing consistent release profiles and dose uniformity.
- Granules and Powders: Our oral solids offerings include granules and powders that are suitable for reconstitution or direct consumption, providing flexibility in administration and catering to various release profile needs.
- Stick Packs: Emphasizing convenience and portability, our oral solids stick packs are an excellent choice for medication on the go, ensuring ease of use and precise dosing.
- Tablets: Our oral solids tablets are available in various shapes and sizes, with customization options such as film-coating, sugar-coating, or enteric-coating to meet specific therapeutic requirements.
- Capsules: The oral solids form of capsules, whether hard or soft gelatin, can be filled with powders, granules, or microgranules, offering a versatile and widely accepted dosage form.
HPAPI Oral Solids
Understanding HPAPIs:
HPAPIs are defined as pharmacologically active ingredients that exhibit biological activity at very low doses, typically at or below 150 µg/kg of body weight in humans. These potent compounds are effective at very low doses, which makes them suitable for oral solid dosage forms like tablets and capsules, providing patients with ease of administration and accurate dosing They are particularly significant in the development of cancer therapeutics, where approximately 60% of approved oncology treatments are based on HPAPIs.
Handling Complexities of Highly Potent Oral Solids: Our Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) is fully equipped to navigate the complexities associated with the handling, development, and production of highly potent oral solids, ensuring that every product meets the rigorous safety and efficacy standards through meticulous process control and quality assurance.
Handling and safety measures are critical to ensure the well-being of workers and the environment, as well as the quality and efficacy of the pharmaceutical products. Here’s a detailed look at these measures:
Handling and Safety Measures:
- Containment: We employ robust containment strategies, such as isolators and contained transfer systems, to protect workers from exposure to HPAPIs and prevent environmental contamination. These systems are critical in maintaining a controlled environment for the safe handling of potent compounds.
- Environmental Monitoring: Our facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art environmental monitoring systems that continuously check for any potential exposure to HPAPIs. This ensures a safe manufacturing environment and helps in immediate response to any containment breaches.
- Equipment: We use dedicated equipment for HPAPI handling to minimize the risk of cross-contamination. This ensures the purity of our oral solids and protects the integrity of our products.
- Training: Our personnel are rigorously trained in HPAPI handling and safety procedures. They are well-versed in the proper use of containment systems and are committed to maintaining the highest safety standards.
Formulation Challenges:
- Solubility and Bioavailability: Addressing the poor solubility and bioavailability of HPAPIs is a common formulation challenge. We utilize specialized techniques, such as particle size reduction and solid dispersion technology, to enhance drug absorption and effectiveness of oral solids.
- Innovative Coating Techniques for Oral Solids: We utilize innovative coating techniques in our oral solids manufacturing, which enhance the stability and release profiles of HPAPIs, providing tailored therapeutic effects.
- Uniform Dosing: Ensuring uniform dosing, especially when dealing with low concentrations of HPAPIs, is critical. Our precision manufacturing processes are designed to deliver consistent and accurate dosing for oral solids.
- Toxicity Data: The development of HPAPIs often faces the challenge of limited toxicity data. We conduct extensive research and risk assessments to ensure safe handling and formulation practices.
- Containment in Formulation: The formulation process for HPAPIs is conducted under strict containment to protect our formulators and manufacturing personnel from exposure, ensuring their safety and the safety of the end product.
Manufacturing Considerations:
- CMC Challenges: The chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) of HPAPIs present unique challenges due to the stringent containment required. We have developed specialized CMC protocols to address these challenges effectively.
- Precision and Control: Our production processes for HPAPIs are characterized by high precision and control. This is essential due to the small quantities of the drug involved and the need for accurate dosing in the final oral solid dosage form.
- Stringent Containment for Oral Solids: We implement stringent containment and control measures in the production of oral solids, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity and quality of high potency active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs), regardless of the batch size.
OSD Manufacturing
Granulation and drying: The granulation and drying unit operation begins to combine the various ingredients and raw materials to create the appropriate granule characteristics for a compressible or encapsulated drug product. This includes dispensing ingredients into the granulation train (wet or dry) and working the materials to achieve the desired results.
A methodology known as dry granulation involves the amalgamation of solid particles through the application of variable intensity motive force, typically executed through high-force compaction within a roller compactor. Unlike conventional wet granulation methods that necessitate the use of binders, dry granulation achieves particle cohesion solely through compaction, yielding dense granules ready for compression or encapsulation.
Dry granulation signifies a departure from traditional wet granulation processes, offering pharmaceutical manufacturers an efficient and binder-free approach to OSD formulation. By eliminating the need for moisture and binders, dry granulation mitigates the risk of chemical instability and contamination, thus enhancing product stability and shelf-life. Additionally, the absence of solvents streamlines the manufacturing process, reducing both production time and environmental impact.
Central to the dry granulation process is the dry granulator system, comprising press rolls and milling mechanisms that facilitate particle compaction and size reduction. Through the adjustment of roll distances, operators can modulate the intensity of compaction, tailoring the characteristics of the resulting granules to meet specific formulation requirements. The roller compactor, serving as the cornerstone of the dry granulation system, applies high shearing forces to the powder blend, promoting particle fusion and densification.
In recent years, advancements in dry granulation technology have led to the development of sophisticated roller compactor designs equipped with enhanced control systems and process monitoring capabilities. Our modern roller compactors offer improved precision and reproducibility that enable us to achieve consistent granule characteristics and dosage uniformity across production batches. Furthermore, the integration of real-time monitoring and data analytics facilitates process optimization and quality assurance, bolstering regulatory compliance and product quality. By using dry granulation, we can enhance product performance, streamline production workflows, and reduce manufacturing costs.
Reasons for Dry Granulation:
1. Dust Reduction: Dry granulation reduces fine particles, enhancing dust control during processing, which is crucial for maintaining a clean and safe working environment.
2. Improved Flowability: By creating denser granules, dry granulation improves the overall flowability of powders. This enhanced flowability is advantageous for downstream processing, facilitating uniform mixing and filling into dosage forms.
3. Particle Size and Uniformity Control: Dry granulation allows for precise control over granule size and distribution, ensuring uniformity in the final product. This control is essential for achieving consistent dosing and desired release profiles.
4. Compaction Enablement: Well-granulated particles hold together effectively during compression into tablet cores, ensuring structural integrity and uniformity in the finished dosage forms.
5. Controlled Solubility Characteristics: Dry granulation enables the manipulation of dissolution profiles by controlling the granule composition and structure. This allows for tailored drug release kinetics, optimizing therapeutic efficacy.
6. Increased Bulk Density: Dry granulation increases the bulk density of granules, a critical parameter for ensuring optimal drug absorption in the body. Higher bulk density enhances packaging efficiency and minimizes dose variability.
Roller compactor: The roller compactor applies motion and energy to integrate and compact solids efficiently and under control. It performs three primary sub-operations: feeding and compacting particles, forming a ribbon of compacted granules, and sizing the granules. It consists of two counter-rotating rollers that apply pressure to the powder feed, forcing it through a narrow gap to form a compacted ribbon. This ribbon is then broken down into granules of desired particle size distributions through milling or sizing mechanisms.
Blending: The blending unit operation combines the active ingredients and excipients and/or lubricants to achieve a homogenous distribution of ingredients. This process may occur more than once in the overall operation. For example, a manufacturer might pre-blend materials prior to granulation and post-blend (or final blend) prior to compression.
Blending unit operation: The blending unit operation combines the active ingredients and excipients and/or lubricants to achieve a homogenous distribution of ingredients. This process may occur more than once in the overall operation. For example, a manufacturer might pre-blend materials prior to granulation and post-blend (or final blend) prior to compression.
Compression and/or encapsulation: This process involves the homogeneous blending of powdered ingredients using only solid materials, typically achieved through gentle tumbling in a blender. The compression and/or encapsulation unit operation creates the final dosage form that patients receive. This step compresses or encapsulates the formulation into the end product: a tablet or capsule. Unlike other granulation methods, direct compression does not involve the use of solvents, heat, or additional binders, making it a preferred choice for certain formulations.
Key Features of Direct Compression:
Homogeneous Ingredient Combination: In direct compression, the uniform blending of ingredients is crucial to ensure consistent distribution of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), excipients, and other components throughout the formulation. Achieving homogeneity is essential for dosage uniformity and product quality.
Preservation of Particle Integrity: Unlike granulation methods that may alter the physical properties of the starting materials, direct compression minimally impacts the integrity of the particles. This is particularly advantageous for formulations containing moisture-sensitive or thermally labile ingredients, as it reduces the risk of degradation and ensures the stability of the final product.
Reasons for Direct Compression:
Ingredient Combination and Homogeneity: Direct compression offers a straightforward and efficient method for blending ingredients, resulting in a homogenous mixture suitable for subsequent processing steps such as tablet compression or encapsulation. This blending process is critical for achieving consistent drug content and uniformity of dosage forms.
Preservation of Particle Integrity: The absence of additional processing steps in direct compression helps preserve the physical properties of the starting granules. This is particularly beneficial for APIs with narrow therapeutic indices or sensitivity to compression forces, as it minimizes the risk of dose variability and ensures product efficacy.
Equipment for Direct Compression:
Tumble Blender: A tumble blender serves as the primary equipment for direct compression, providing gentle mixing and blending of powdered ingredients. These blenders come in various configurations, including V-shaped and double cone designs, allowing for efficient blending of different batch sizes and formulations. Advanced tumble blenders may incorporate features such as baffles or intensifier bars to enhance mixing efficiency and reduce blend segregation.
Charging and Discharging Equipment: Auxiliary equipment such as charging and discharging systems play a crucial role in the direct compression process by facilitating the loading of materials into the blender and the removal of the blended mixture after processing. These systems are designed to ensure accurate dosing, minimize cross-contamination, and maintain process integrity throughout the manufacturing cycle.
Tablet coating: One of the final steps in the OSD manufacturing process is tablet coating. After a core tablet has been compressed, a film or functional coat is applied to the tablet. This improves the taste and makes the tablet easier to swallow. A functional coating is also common. This is an additional active ingredient applied to the outside of the tablet.
Modern Particle Coating: Advancing Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
Emergence of Fluid Bed Processing: The mid-20th century witnessed the emergence of fluid bed processing as a revolutionary technique for particle coating. Fluid bed coaters provided a more precise and efficient means of applying coatings to pharmaceutical granules, enabling greater control over coating thickness and uniformity.
Advancements in Spray Atomization: With the advent of spray atomization technology in the latter half of the 20th century, particle coating saw further refinements. Atomized liquid to powder coating in fluid bed processors became the gold standard, offering unparalleled precision and reproducibility in coating applications
Particle coating offers a versatile method for encapsulating active ingredients within protective layers. This process seamlessly combines liquids and solids using a gentle, low-intensity motive force, typically through atomized liquid to powder coating in a fluid bed processor. By enveloping individual granules or beads with precise coatings, particle coating facilitates the creation of capsule dosage forms with enhanced stability, controlled release, and improved patient acceptability.
Key Features of Particle Coating:
Enhanced Encapsulation: Particle coating involves precisely applying an active drug and/or sealer onto individual granules or beads, creating a protective barrier that shields the active ingredient from environmental factors while enabling controlled release upon administration.
Spray Atomization Configuration: Employing a spray atomization configuration ensures uniform deposition of liquid and solid suspensions onto granules or beads within the fluid bed processor. This gentle interaction between the solution and dry particles guarantees the formation of smooth, uniform coatings essential for optimal performance.
Benefits of Particle Coating:
Low Abrasion, Smooth Surface: Coated particles exhibit reduced abrasiveness and boast a smooth surface texture, enhancing flowability and minimizing wear on processing equipment, thus ensuring consistent manufacturing efficiency.
Taste and Odor Masking: Particle coatings effectively mask the taste and odor of active ingredients, improving patient compliance and acceptability of oral dosage forms, particularly for pediatric and geriatric populations.
Environmental Protection: Coatings offer robust protection against light, air, and moisture, safeguarding the stability and potency of encapsulated active ingredients throughout storage and transportation.
Multi-layer Formulations: Particle coating facilitates the creation of multi-layer compositions, enabling the incorporation of successive layers with distinct functionalities. These layers may provide delayed release, targeted delivery, or additional protective barriers against environmental factors, enhancing the versatility and efficacy of dosage forms.
Equipment Used for Particle Coating:
Fluid Bed Coater: Serving as the primary equipment for particle coating, the fluid bed coater enables precise integration of solids and liquids while maintaining optimal control over processing parameters. Unlike compression-based methods, the fluid bed coater utilizes spray atomization and drying processes to create uniform layers of coatings on granules or beads.
Solution Delivery System and Dryer: Integral components of the particle coating process, the solution delivery system accurately dispenses liquid solutions onto the granules or beads, while the dryer facilitates rapid evaporation of solvents to achieve desired coating characteristics. These systems ensure uniform coating distribution and consistency across batches, contributing to the overall quality and performance of the final dosage forms.
Additional Benefits
Large and Flexibly Manufacturing Capacity:
Our facility can handle billions of units of production for oral solid dosage forms.
Packaging, Labeling, and Serialization:
We provide comprehensive end-to-end solutions for the packaging, labeling, and serialization of oral solids. Our services cater to both clinical and commercial OSD manufacturing, accommodating various packaging formats. Our advanced serialization services for oral solids ensure compliance with global regulatory requirements, offering our partners complete peace of mind.
Innovative Delivery Technologies:
Innovation is at the heart of our approach to oral solids. We employ various delivery technologies, including sustained-, pulsed-, modified-, and delayed-release, to enhance the therapeutic effectiveness and patient convenience of your drug product. Additionally we can utilize various nanotechnologies and lipid based drug delivery solutions to enhance your molecules bioavailability and efficacy.
Quality Control and Analytical Development for Oral Solids:
Our facilities feature cutting-edge quality control and microbiology labs dedicated to oral solids. Alongside our preformulation and analytical development infrastructure, we ensure that every OSD meets stringent safety, efficacy, and quality standards.
Research and Development:
Our R&D pilot lab is pioneering the next generation of oral solids. We work in close collaboration with our partners to develop oral solid formulations that address specific therapeutic needs and market demands.
Temperature-Controlled Warehousing:
To preserve the integrity of your oral solid drug products, we offer temperature-controlled warehousing solutions. This ensures that your OSDs are stored under optimal conditions, maintaining their quality throughout the supply chain.
Services






FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Oral Solids
Oral solid dosage forms include tablets, capsules, powders, and granules. They are the most popular method of drug delivery due to their convenience, stability, and ease of mass production. These forms allow for precise dosages, extended shelf life, and improved patient compliance, making them a staple in both over-the-counter and prescription medication markets.
We offer comprehensive services for oral solid dosage forms, including formulation development, process optimization, scale-up, and manufacturing. Our capabilities extend to immediate and controlled-release formulations, coating, encapsulation, and the development of chewable, dispersible, and effervescent tablets. We also provide packaging and analytical testing services to ensure product quality and compliance.
Quality and compliance are paramount in our operations. We adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and are regularly inspected by regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA. Our quality control processes include rigorous testing of raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products. We also implement robust quality assurance protocols, including validation and stability studies, to ensure our products meet all regulatory standards.
Yes, we have specialized facilities and containment systems designed to safely handle controlled substances. Our team is experienced in managing the unique challenges associated with these substances, including stringent regulatory requirements and the need for specialized equipment and safety protocols.
Our production capacity is flexible and scalable to meet the needs of our clients, ranging from small-scale batch production for clinical trials to large-scale manufacturing for commercial supply. Our facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art machinery for granulation, compression, and coating, allowing us to efficiently produce a wide range of batch sizes with high precision and consistency.
For generic products, we focus on bioequivalence studies, cost-effective formulation, and process optimization to ensure competitive market entry. For novel oral solid dosage forms, we collaborate closely with our clients to develop innovative formulations that enhance bioavailability, improve patient compliance, and extend product lifecycle, leveraging our expertise in drug delivery technologies and formulation science.
Our formulation development and optimization process is data-driven and collaborative. We utilize Quality by Design (QbD) principles, incorporating thorough understanding of the drug substance, target product profile, and manufacturing processes. We employ advanced modeling and simulation tools, along with high-throughput screening methods, to rapidly identify and optimize formulations that meet the desired product attributes.
Project management is a core competency of our operations. We assign dedicated project managers to each client, who oversee all aspects of the project from inception to delivery. Our project managers work closely with clients to establish clear timelines, milestones, and communication plans. We utilize agile manufacturing practices and real-time monitoring to ensure projects remain on track and adjustments are made proactively to meet delivery commitments.
While confidentiality agreements restrict the details we can share, we have successfully partnered with numerous pharmaceutical companies to bring both generic and innovative oral solid dosage products to market. Our collaborations often involve overcoming complex formulation challenges, scaling up novel production processes, and navigating regulatory approvals efficiently.
Starting a project with us is straightforward. Interested pharmaceutical companies can contact us through our website, email, or phone to schedule an initial consultation. During this consultation, we discuss the project scope, objectives, and timelines. Following this, we provide a proposal outlining our services, timelines, and cost estimates. Upon agreement, we initiate the project with a kick-off meeting to align on project details and establish communication protocols.