Many people to die from cardiometabolic diseases such as heart attack, stroke, diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. These conditions are not only common but also largely preventable, yet they continue to be leading causes of death worldwide. Our mission is to support pharmaceutical innovators and researchers in their quest to understand the underlying causes of these diseases. By providing cutting-edge manufacturing and development services, we aim to accelerate the creation of effective treatments.
The socioeconomic impact of cardiometabolic conditions is profound, affecting countries at all income levels. The cost of healthcare, loss of productivity, and the burden on families and communities is immense. We are committed reducing this burden by:
- Collaborating with our pharmaceutical partners to develop preventative therapies that can mitigate risk factors.
- Innovate in the formulation and manufacturing of medications that can manage and treat these diseases effectively.

Our Mission
Our Pharmacists and R&D Pharmaceutical scientists are dedicated to understanding the pathophysiology of cardiometabolic diseases. Our ultimate goal is to reduce the mortality associated with these preventable conditions and contribute to the health and well-being of communities now and in the future.
Related Services




FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about softgels.
Softgel capsules are a form of liquid-filled capsules made from a gelatin-based shell surrounding a liquid or semi-solid fill. Unlike hard-shell capsules, which are composed of two rigid halves, the softgel's shell is flexible and seamless, offering a unique dosage form for a wide range of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Softgels are valued for their ability to encapsulate high-potency drugs, improve bioavailability, and mask unpleasant tastes and odors.
Softgels can enhance drug bioavailability by encapsulating the drug in a liquid form, which can be more readily absorbed by the body compared to solid dosage forms. The liquid fill can contain solubilized APIs, which are especially beneficial for poorly water-soluble drugs, facilitating faster dissolution and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. Additionally, the formulation flexibility allows for the inclusion of solubilizers and emulsifiers to further improve the dissolution rate and absorption of the encapsulated drug.
Softgel encapsulation is suitable for a wide range of APIs, including lipophilic (fat-soluble) compounds, poorly water-soluble drugs, liquids, and semi-solids. Softgels are particularly advantageous for APIs that require stabilization or are sensitive to oxygen or light, as the encapsulation offers a protective environment. This dosage form is versatile enough to accommodate various therapeutic categories, including vitamins and supplements, analgesics, antifungals, and cardiovascular drugs.
Yes, softgels can be formulated for controlled-release applications. By manipulating the gelatin shell composition and the fill formulation, it's possible to achieve various release profiles, including delayed-release, sustained-release, and targeted-release. These modifications allow for the precise control of drug release rates, enhancing therapeutic outcomes and patient compliance by reducing dosing frequency.
Softgels offer several advantages over other dosage forms, including:
Improved Patient Compliance: Their smooth, flexible shape makes them easier to swallow compared to tablets or capsules.
Bioavailability Enhancement: The liquid fill can improve the absorption of poorly soluble drugs.
Taste Masking: The encapsulation masks the taste and odor of unpleasant APIs.
Protection of Sensitive Ingredients: The shell provides a barrier against light, oxygen, and moisture.
Dose Precision: Each softgel contains a precisely measured dose, reducing variability.
Aesthetic Appeal: Softgels are available in various shapes, sizes, and colors, enhancing patient acceptance.
Key considerations in softgel formulation development include:
API Solubility: Ensuring the API is adequately soluble in the fill material to achieve the desired bioavailability.
Shell Composition: Selecting the appropriate gelatin type or alternative polymers to meet dietary or stability requirements.
Fill Excipients: Choosing excipients that enhance the API's stability and absorption without compromising the integrity of the shell.
Sealing Technology: Employing robust sealing techniques to prevent leakage and ensure product stability.
Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the API, excipients, and shell materials to maintain efficacy and extend shelf life.
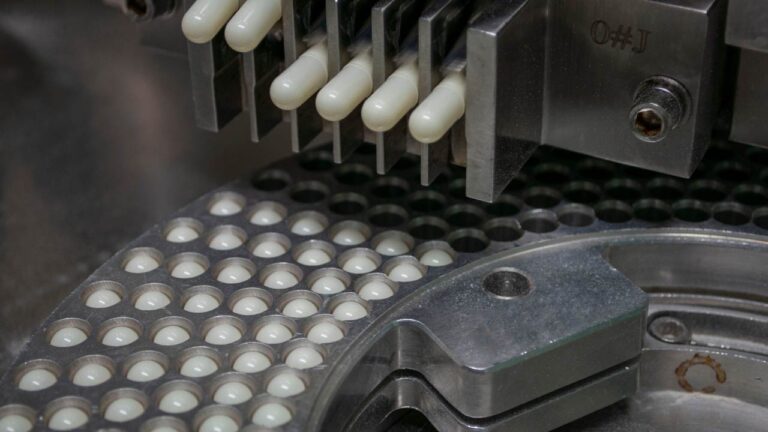
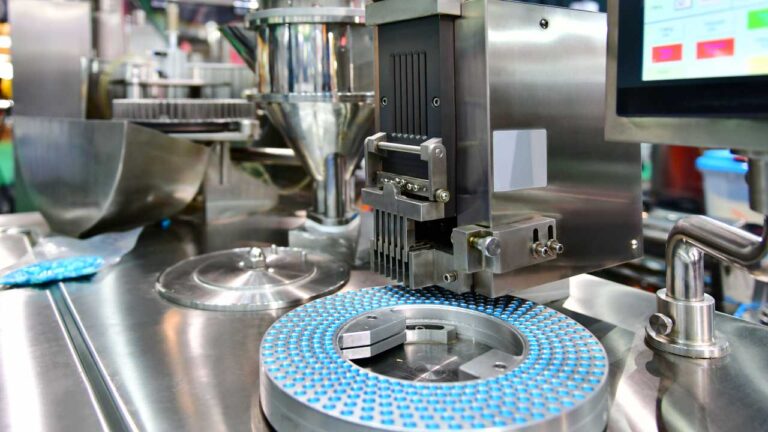
Softgel capsules are manufactured using a rotary die process, where gelatin is heated and molded into two ribbons that form the capsule shell. The liquid or semi-solid fill is simultaneously injected between these gelatin ribbons, and the capsules are sealed and shaped by the dies. The capsules are then cooled, trimmed, and inspected for quality before packaging. This process requires precise control of temperature, humidity, and fill volume to ensure consistent product quality.
Yes, softgels are an excellent choice for combination therapies, as they can encapsulate multiple APIs within the same capsule. This capability allows for the combination of drugs with complementary therapeutic effects or the inclusion of both immediate-release and controlled-release components in a single dosage form. Combination therapy softgels can simplify treatment regimens, improving patient compliance and therapeutic outcomes.
Softgels can be packaged in a variety of containers, including blister packs, bottles, and pouches, depending on the product's stability requirements and marketing considerations. Packaging is selected based on factors such as moisture sensitivity, light protection, and consumer convenience. Additionally, tamper-evident and child-resistant features can be incorporated to ensure product safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Hycon ensures the quality and stability of softgel capsules through rigorous quality control and stability testing procedures. This includes:
Raw Material Testing: Verifying the purity and quality of gelatin, APIs, and excipients.
Process Control: Monitoring manufacturing conditions to maintain consistent shell thickness, fill volume, and seal integrity.
Finished Product Testing: Conducting physical, chemical, and microbiological tests to confirm capsule uniformity, API content, and dissolution characteristics.
Stability Studies: Assessing the product's shelf life under various environmental conditions to determine appropriate storage recommendations and expiration dating.