Transdermal patches are a form of drug delivery system wherein the medication, embedded in an adhesive matrix, is absorbed through the epidermal layers, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract entirely. This method not only minimizes the risk of gastrointestinal irritation or degradation of the active pharmaceutical ingredient but also contributes to a more consistent and controlled release of the drug, thereby enhancing overall therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance.
Our expertise encompasses small molecules—such as those characterized by their insolubility or representing novel chemical entities—and controlled substances that are classified under the schedules of I through V. The challenge of formulating these various drug types requires a meticulous approach to ensure their effective and safe delivery through the skin.
We utilize a diverse range of excipients including emulsifiers, which are crucial for stabilizing and mixing ingredients that are typically immiscible; stabilizers, which help in maintaining the integrity and potency of the drug over time; penetration enhancers, which facilitate the active ingredient’s ability to traverse the stratum corneum and reach systemic circulation; and emollients, which improve skin hydration and comfort to support the overall effectiveness of the transdermal patch.

How Transdermal Patches Work?
- Mechanism of Action: Transdermal patches operate by embedding medication within a delicate, adhesive layer that forms a secure bond with the skin. This adhesive layer is meticulously designed to release the drug in a controlled manner, facilitated by a backing membrane that regulates the rate of drug diffusion. The backing membrane acts as a barrier, ensuring that the medication is delivered gradually and consistently through the skin over an extended period. The intricate design of these patches allows for a precise modulation of drug release, maintaining a steady therapeutic level of medication in the bloodstream and optimizing the treatment outcome.
- Advantages: Transdermal patches present numerous benefits compared to conventional oral medications. One significant advantage is the avoidance of first-pass metabolism, a process where the drug is metabolized by the liver before reaching systemic circulation, which can significantly diminish its efficacy. By bypassing this metabolic pathway, transdermal patches enable a more effective delivery of medication. Additionally, these patches provide consistent plasma drug levels, which helps in maintaining stable therapeutic effects and reducing the likelihood of peak-and-trough fluctuations that are often observed with oral dosing. Furthermore, the simplicity of application and the convenience of having a patch adhered to the skin contribute to enhanced patient compliance, as it eliminates the need for frequent dosing and minimizes the risk of forgetting doses.
- Drug Formulation: The formulation of drugs for use in transdermal patches is a crucial and complex process. It often involves incorporating permeation enhancers, which are specialized compounds that facilitate the movement of the drug through the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the skin. These enhancers work by temporarily disrupting the lipid structure of the skin, allowing the drug to penetrate more effectively. The drug formulation must also ensure stability and compatibility with the adhesive and backing materials, and it should be optimized to maintain the drug’s potency and efficacy over the duration of the patch’s use. This formulation process is critical in achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the transdermal delivery system.
- Application Sites: For optimal performance, transdermal patches should be applied to clean, dry, and hairless areas of the skin. Areas with minimal movement, such as the upper arm, chest, or back, are ideal for application as they provide a stable surface that enhances both drug absorption and patch adhesion. The skin should be free of any lotions, oils, or other substances that could interfere with the adhesive properties of the patch. Proper site selection is crucial to ensure that the patch remains securely in place, which is vital for maintaining consistent drug delivery and preventing issues such as peeling or detachment.
- Duration of Use: Transdermal patches are designed with varying durations of use, tailored to the specific medication and therapeutic goals. They can be engineered for short-term applications lasting a few hours or for extended periods spanning several days. This flexibility allows for controlled and sustained medication delivery, aligning with the treatment regimen prescribed by healthcare providers. The duration of use is carefully calibrated based on the medication’s pharmacokinetics and the desired therapeutic effect, providing a balanced approach to drug administration that enhances patient convenience and adherence.
- Patient Education: Educating patients on the proper use of transdermal patches is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and minimizing potential side effects. Patients should be instructed on the correct application techniques, including how to ensure the patch adheres securely and how to avoid areas of the skin that may not provide optimal adhesion. Additionally, guidance on rotating application sites is important to prevent skin irritation and ensure even drug absorption. Instructions for the proper disposal of used patches should also be provided to avoid any environmental impact or accidental exposure to others. Effective patient education plays a critical role in optimizing the therapeutic benefits of transdermal patches and enhancing overall treatment outcomes.
- Potential Side Effects: Although transdermal patches are designed to reduce gastrointestinal side effects commonly associated with oral medications, they may still induce local skin reactions at the site of application. Potential side effects include redness, itching, or irritation, which can occur due to the adhesive or the drug itself. In some cases, patients may experience more pronounced skin reactions, necessitating the need for appropriate management strategies. It is important for patients to report any adverse reactions to their healthcare provider, who can offer guidance on mitigating these effects and, if necessary, suggest alternative treatment options.
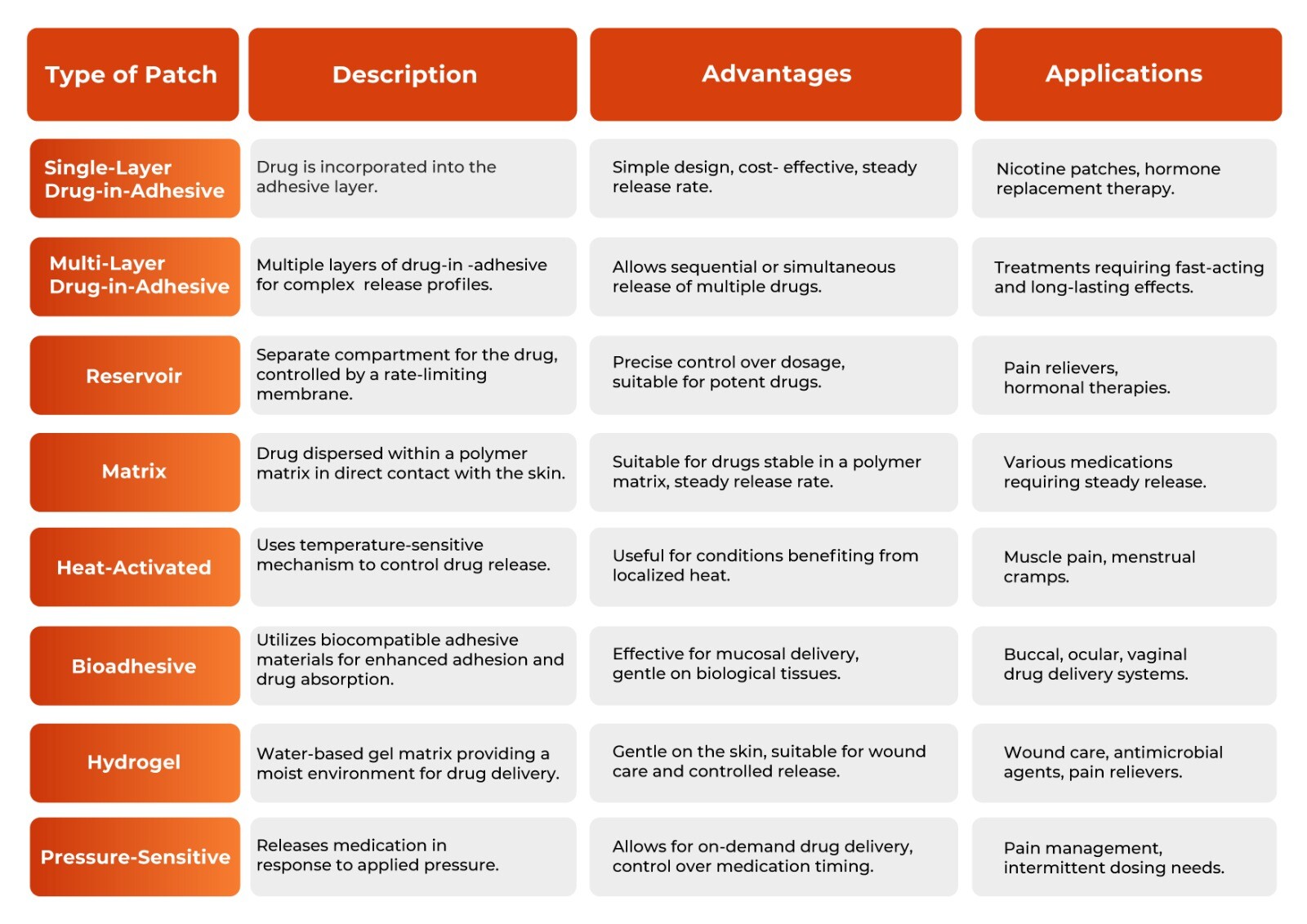
Transdermal Patch Type Comparisons
Transdermal Patches Design And Development Process
Controlled Drug Release: Transdermal patches are meticulously engineered devices designed to administer medication at a highly consistent and controlled rate over an extended period. This sophisticated approach to drug delivery ensures that medication is released into the bloodstream at a steady and predetermined rate, maintaining stable drug levels for the exact duration required for therapeutic efficacy. By precisely controlling the release kinetics, transdermal patches provide a reliable therapeutic effect, mitigating the fluctuations often associated with other drug delivery methods that can lead to suboptimal therapeutic outcomes.
Mixing/Blending: The initial phase in the manufacturing of transdermal patches is the meticulous process of mixing the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) with various excipients. This blending process is critical because it ensures that the API is uniformly distributed throughout the formulation, which is essential for achieving a consistent and reliable performance of the transdermal patches. The homogeneity of the drug formulation directly affects the efficacy and safety of the patch, as any uneven distribution of the API can lead to variability in drug release rates and potentially impact patient outcomes. The selection of appropriate excipients and the precision in their incorporation play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and effectiveness of the final product.
Multi-Layered Construction: Our transdermal patches are engineered with a sophisticated multi-layered construction that enables the creation of separate drug reservoirs within a single patch. This advanced design facilitates combination therapy by allowing the simultaneous delivery of multiple drugs or active substances, each from its distinct reservoir. Additionally, the multi-layered construction permits the tailoring of release profiles, making it possible to develop complex treatment regimens that cater to specific therapeutic needs. This approach enhances the versatility of the transdermal patch, allowing it to be adapted for various medical conditions and patient requirements.
Skin-Friendly Adhesives: The adhesives used in the formulation of transdermal patches are carefully selected for their compatibility with the skin to ensure optimal adhesion without causing irritation or discomfort. These skin-friendly adhesives are formulated to adhere securely to the skin throughout the duration of use while maintaining the integrity of the patch’s delivery system. The choice of adhesive materials is crucial as it affects not only the effectiveness of the drug delivery but also the comfort and safety of the patient. The adhesives must be robust enough to prevent the patch from shifting or falling off but gentle enough to avoid causing skin reactions or discomfort.
Integrated Release Liners: Transdermal patches are designed with integrated release liners that serve as a protective barrier during storage and handling. These release liners are engineered to be easily removable by patients, simplifying the application process and making it more user-friendly. By incorporating this feature, the patch can be applied quickly and efficiently, enhancing patient compliance and ensuring that the medication is delivered accurately. The convenience of the integrated release liners contributes to a smoother initiation of therapy and minimizes the risk of errors in patch application.
Coating: The process of coating the drug formulation onto a suitable backing layer is a critical step in the production of transdermal patches. This coating process is meticulously controlled to ensure that the medication is evenly distributed across the backing layer, which is essential for the controlled release of the drug. The uniformity of the coating impacts the efficacy of the patch by regulating the rate at which the medication is released into the skin. This controlled release mechanism is a hallmark of the efficacy of transdermal patches, ensuring that the medication is delivered at a consistent rate over time.
Converting/Packaging: Following the coating process, the material is converted into individual transdermal patches, each designed to deliver a precise dose of medication. The conversion process involves cutting and shaping the coated material into the final patch form. Once converted, the patches are carefully packaged to preserve their integrity and efficacy until the point of use. The packaging is designed to protect the patches from environmental factors such as moisture and light, which could otherwise degrade the medication. Proper packaging is essential for maintaining the quality and effectiveness of the transdermal patches throughout their shelf life.
Innovative Materials: The development of transdermal patches often involves the use of innovative materials that enhance various aspects of the patch’s performance. These materials are selected to improve drug stability, ensure better skin adherence, and maximize patient comfort during wear. Innovations in materials science contribute to the advancement of transdermal patch technology by addressing challenges such as drug degradation, skin irritation, and the need for extended wear times. By incorporating cutting-edge materials, manufacturers can enhance the overall efficacy and user experience of transdermal patches.
Customization Options: Transdermal patches offer a range of customization options, including variations in size, shape, and dosage, to meet the specific needs of different patient populations and therapeutic requirements. Customization allows for the development of patches that are tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring that the drug delivery system is optimized for the intended treatment. This flexibility in design helps address a wide range of medical conditions and allows for personalized therapy, enhancing the overall effectiveness and acceptance of transdermal patch technology.
Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of transdermal patches is an important consideration in their design and production. Efforts are made to minimize waste generated during the manufacturing process and to ensure the safe disposal of used patches. Sustainable practices may include using eco-friendly materials and reducing the environmental footprint of packaging. By addressing environmental concerns, manufacturers aim to contribute to the broader goal of reducing the ecological impact of medical products and promoting responsible use of resources.
Patient Education Materials: Comprehensive patient education materials are provided alongside transdermal patches to ensure that patients are well-informed about the proper usage of the patches. These materials include instructions on how to apply and remove the patch, guidelines for site rotation, and information on adherence to prescribed therapy. Providing clear and thorough education helps patients use the patches correctly, which is crucial for achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential issues related to incorrect usage.
Clinical Trials: Transdermal patches undergo rigorous clinical trials to evaluate their safety, efficacy, and potential advantages over other drug delivery methods. These trials involve extensive testing to confirm that the patches deliver the medication effectively and safely. Clinical trials are conducted to ensure that the patches meet regulatory standards and demonstrate superior performance in treating specific medical conditions. The results of these trials provide valuable information that guides further development and helps establish the clinical benefits of transdermal patch technology.
Market Analysis: Ongoing market analysis plays a crucial role in understanding the demand for transdermal patches and guiding future developments in this field. Market analysis involves studying trends, assessing competitive products, and identifying emerging needs and opportunities. This information helps manufacturers and developers make informed decisions about product innovations, improvements, and strategic planning. By staying attuned to market dynamics, companies can better align their offerings with patient needs and industry advancements, driving continued progress in transdermal drug delivery technology.
Patient-Centricity
Understanding that many of our patients lead active lifestyles, Hycon has developed transdermal patches with superior water resistance. This vital feature permits patients to engage in a variety of activities, including swimming, showering, and vigorous exercise, without diminishing the effectiveness of the medication. The water-resistant nature of our patches ensures that they remain securely in place and continue to deliver medication effectively, regardless of the patient’s level of physical activity.
The safety and well-being of our patients are of utmost importance to us. To this end, Hycon’s transdermal patches are manufactured using hypoallergenic materials. These materials are specifically chosen to minimize the risk of allergic reactions and skin sensitivities, providing a comfortable and irritation-free experience for patients. Our commitment to using hypoallergenic components ensures that even those with sensitive skin can benefit from our treatment without adverse effects.
Engineered for extended wear, Hycon’s transdermal patches offer consistent and reliable medication delivery over prolonged periods. This design is particularly advantageous for managing chronic conditions that require a steady and continuous dosage of medication. By extending the wear time, our patches reduce the need for frequent application, thereby improving patient compliance and simplifying the management of long-term treatments.
Ease of use is a cornerstone of our patch design. The application and removal processes are straightforward, making Hycon’s transdermal patches user-friendly for all patients, including the elderly or those with limited dexterity. The simplicity of handling our patches helps ensure that patients can adhere to their treatment regimen with minimal effort and without requiring assistance.
We incorporate advanced drug formulations into our transdermal patches. This approach enhances the bioavailability and overall efficacy of the medications delivered, ensuring that patients receive optimal therapeutic benefits. Our commitment to integrating cutting-edge formulations helps to maximize the effectiveness of our treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Recognizing that each patient’s needs are unique, Hycon offers customized dosages in our transdermal patches. This personalization allows for precise medication management tailored to individual requirements, providing a more effective treatment approach and ensuring that patients receive the exact dosage needed for their specific condition. To safeguard the well-being of all patients, especially young children, Hycon ensures that all transdermal patches are packaged in child-resistant containers. This precaution helps to prevent accidental ingestion or misuse of the patches, thus promoting a safer environment and reducing the risk of unintended exposure.
Additional Benefits
Customized Development for Niche Markets
We take a specialized approach in creating transdermal patches specifically designed for niche markets. Our core expertise is concentrated on developing patches that cater to the unique needs of pediatric and geriatric populations, as well as individuals with particular medical conditions. We are dedicated to creating patient-centric designs that prioritize ease of use and adherence, ensuring that our patches are not only effective but also user-friendly. By focusing on these niche markets, Hycon tailors solutions that address the diverse requirements of different patient groups, facilitating improved therapeutic outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Innovative Skin Technology
At the forefront of transdermal patch development, we harnesses the latest advancements in skin technology to significantly boost the efficacy of our products. Our research and development team innovative meth explores ds to overcome the inherent challenges associated with penetrating the skin barrier. Through meticulous research, we enhance drug permeation rates, ensuring that our transdermal patches deliver consistent and effective drug release. This commitment to leveraging cutting-edge skin technology allows us to address complex pharmacokinetic issues and optimize therapeutic performance.
Performance Testing and Validation
Hycon prides itself on its state-of-the-art testing facilities, which are equipped with advanced capabilities to thoroughly validate the performance of our transdermal patches. We conduct extensive in vitro release testing (IVRT) and in vitro permeation testing (IVPT) to rigorously evaluate drug delivery consistency and maintain therapeutic levels. These comprehensive tests are critical for confirming that our patches function as intended, delivering the right dose of medication over the prescribed period and ensuring that our products meet the highest standards of efficacy and safety.
Transdermal Patch Manufacturing Process Excellence
- Mixing/Blending: Precision in the mixing and blending of active ingredients is a fundamental aspect of our transdermal patch manufacturing process. We employ sophisticated techniques to ensure that each component is uniformly distributed, thereby guaranteeing that the final product delivers a consistent therapeutic dose.
- Coating Technologies: Our commitment to excellence is evident in our use of advanced coating technologies, which are crucial for achieving uniform drug distribution across each transdermal patch. These technologies are designed to enhance the release profile of the drug, ensuring that it is delivered steadily and reliably over time.
- Converting and Packaging: The converting and packaging stages of our manufacturing process are meticulously designed to preserve the integrity of the transdermal patches. We implement stringent procedures to maintain product quality and facilitate efficient distribution, ensuring that each patch reaches the market in optimal condition.
Regulatory and Compliance Expertise
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape is an area where Hycon excels with confidence and precision. Our team possesses extensive expertise in ensuring that all our transdermal patches comply with rigorous regulatory standards for safety and efficacy. We stay abreast of evolving regulations and requirements, ensuring that our products meet the highest standards set by regulatory authorities. This dedication to compliance underscores our commitment to delivering safe and effective transdermal solutions.
End-to-End Project Management
Hycon offers a comprehensive suite of project management services designed to oversee the entire lifecycle of your transdermal patch development. From the initial concept through to market launch, our project management approach ensures a seamless progression through each stage of development and manufacturing. We provide transparent communication and detailed timelines, allowing for efficient coordination and execution of every phase of the project. This end-to-end service is aimed at delivering high-quality products on schedule and within budget, aligning with the specific needs and expectations of our clients.
Related Services




FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Transdermal Patches
Transdermal patches are medicated adhesive patches designed to deliver a specific dose of medication through the skin and into the bloodstream. They work by providing a controlled release of drugs over an extended period, ensuring a consistent therapeutic level in the body. This is achieved through a combination of the patch's adhesive properties, the permeability of the skin, and the drug's formulation, which together facilitate the drug's absorption into the systemic circulation.
A wide variety of drugs can be delivered through transdermal patches, including but not limited to hormones (such as estrogen and testosterone), pain relievers (such as fentanyl), nicotine (for smoking cessation), and cardiovascular drugs (such as nitroglycerin). The suitability of a drug for transdermal delivery depends on its molecular weight, solubility, potency, and the drug's ability to penetrate the skin barrier.
Transdermal patches offer several advantages, including:
Improved Compliance: Easy to use and requiring less frequent dosing than oral medications or injections.
Steady Medication Levels: Provides a controlled release of medication, which helps maintain consistent drug levels in the bloodstream.
Reduced Side Effects: Minimizes the risk of gastrointestinal side effects and avoids the first-pass metabolism in the liver, potentially reducing the overall side effect profile.
Non-Invasive: Offers a needle-free alternative to injections, improving patient comfort.
Formulating oral suspensions and solutions involves several key considerations, including solubility enhancement, taste masking, viscosity adjustment, and preservative efficacy. The formulation must ensure physical and chemical stability, acceptable palatability, and compliance with regulatory requirements. The choice of excipients and the manufacturing process must also be optimized to ensure product quality and consistency.
Quality and safety of transdermal patches are ensured through rigorous testing and quality control measures, including:
Raw Material Testing: Screening all materials used in the patch for purity and safety.
Process Validation: Validating manufacturing processes to ensure consistent product quality.
Release Testing: Testing each batch for drug content, adhesion properties, and drug release rate.
Stability Testing: Assessing the product's stability under various environmental conditions to determine shelf life.
Clinical Trials: Conducting clinical trials to evaluate the patch's safety and efficacy in humans.
Manufacturing transdermal patches involves compliance with regulatory requirements set by health authorities such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and EMA
(European Medicines Agency). Key considerations include:
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Adhering to GMP guidelines to ensure product quality and safety.
Submission of Regulatory Dossiers: Preparing and submitting detailed information on the patch's formulation, manufacturing process, quality control, and clinical data.
Post-Market Surveillance: Monitoring the product's performance and safety after market approval.
Yes, transdermal patches can be engineered to provide various release profiles, including immediate release, delayed release, or sustained release, depending on the therapeutic needs. This is achieved through adjustments in the formulation, the design of the drug reservoir, and the selection of the rate-controlling membrane or adhesive.
Formulating transdermal patches presents several challenges, such as:
Skin Barrier Penetration: Enhancing the drug's ability to penetrate the skin barrier without causing irritation or damage.
Drug Stability: Ensuring the stability of the drug within the patch environment over its intended shelf life.
Adhesive Selection: Choosing an adhesive that ensures the patch remains securely attached to the skin while not causing irritation or allergic reactions.
Controlled Release: Achieving a consistent and controlled release rate of the drug over the patch's active life.
Transdermal patches are tested for efficacy and safety through a combination of in vitro studies, animal studies, and clinical trials in humans. These tests evaluate the patch's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, adhesion properties, skin irritation potential, and overall therapeutic effectiveness. Regulatory authorities require comprehensive data from these tests before granting approval for market release.
CDMOs offer a range of support services for transdermal patch development, including:
Product Development: Assistance with formulation, process development, and design optimization.
Analytical Services: Comprehensive testing services for drug content, release rates, and stability.
Regulatory Support: Guidance on regulatory strategy, dossier preparation, and submission to regulatory agencies.
Manufacturing Services: Scale-up and commercial manufacturing capabilities, including packaging and quality control.