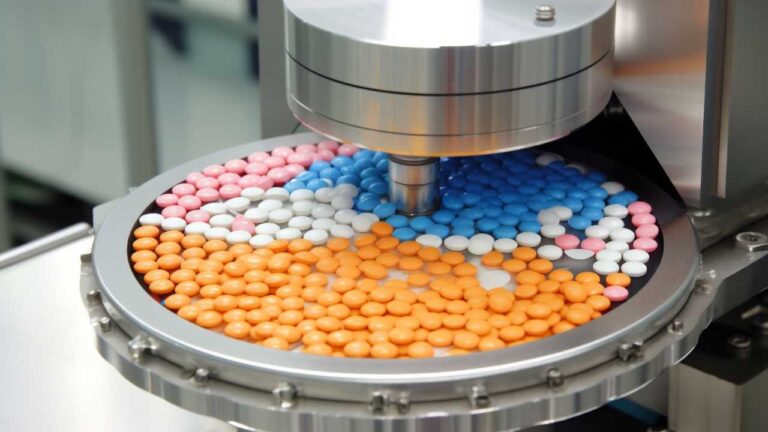
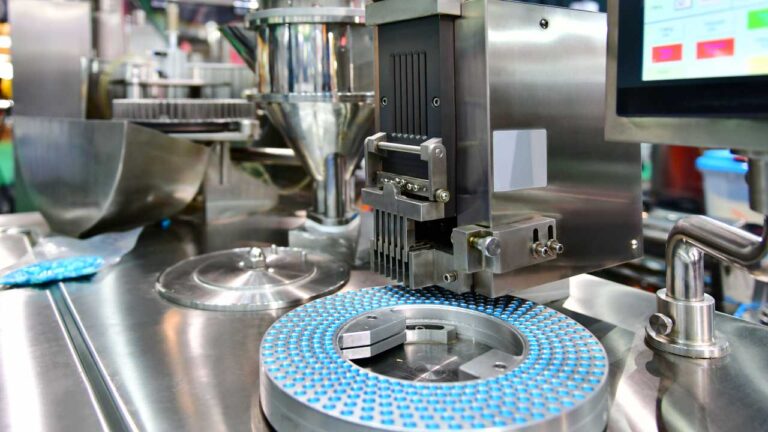
Hormonal formulations are drug products that contain a combination of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), specifically hormones, along with other inactive components. These formulations come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, liquids, and injectables. They can be used alone as a primary treatment or in conjunction with other treatments. For instance, hormonal formulations may be administered before surgery to shrink a tumor, making it easier to remove, or before radiation therapy to target a smaller area.
Hormones are chemical substances produced by the body that regulate the activity of specific cells or organs. They are secreted by specialized glands, such as the thyroid gland, which produces thyroid hormone. Hormones are crucial for numerous bodily functions, including digestion, metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood regulation. Many hormones, like neurotransmitters, are involved in multiple physiological processes.

What are hormone APIs?
Examples of Hormones
- Corticosteroid (Steroid) Hormones: Synthetic drugs resembling cortisol, a naturally occurring hormone. They reduce inflammation and immune system activity and are available in various forms, including pills, inhalers, nasal sprays, creams, and ointments.
- Thyroid Hormones: Produced by the thyroid gland, these hormones regulate metabolism and energy levels.
- Somatostatin Analogues: Used to treat conditions like acromegaly and certain types of tumors.
- Sex (Reproductive) Hormones: Including androgens, estrogens, progestins, anti-androgens, anti-estrogens, and aromatase inhibitors.
Steroid Hormones
Steroids, short for corticosteroids, are synthetic drugs that closely resemble cortisol, a hormone that our bodies produce naturally. Steroids work by decreasing inflammation and reducing the activity of the immune system. They come in pill form (steroid capsules), as inhalers or nasal sprays, and as creams and ointments. Various contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) offer outsourcing services for the production of steroid capsules, which are powerful medicines taken to reduce the swelling and inflammation of airways.
Uses of Hormonal Formulations
Hormonal formulations or hormone pills can be administered as a treatment option for anyone with hormonal imbalances, including but not limited to:
- Levothyroxine: Medications containing levothyroxine, such as Synthroid and Levothroid, can help improve symptoms of hypothyroidism.
- Estrogen Therapy: Treatment for menopause.
- Anti-androgen Medications: Women with high androgen levels may choose to take hormone pills as medication that blocks the effect of androgens.
- Testosterone Therapy: Testosterone supplements can reduce the symptoms of low testosterone in men.
- Hormonal Birth Control: Hormonal birth control can help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Hormonal Therapy (Oncology): A treatment that adds, blocks, or removes hormones to slow or stop the growth of cancer cells. Hormonal therapy is also called hormone withdrawal therapy, hormone manipulation, or endocrine therapy.
What are the different components (ingredients) of hormonal capsules
Hormonal capsules contain hormones as active pharmaceutical ingredients along with other additives in a soft or hard capsule shell. The various components of hormonal capsules are discussed below.
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in hormonal capsules are synthetic versions of hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone (steroidal hormones).
Inactive Components
- Gelatin: (E.g., Bovine, Porcine, Piscine) Gelatin is an animal protein made by boiling the collagenous material from animal bones, hides, and skin. Depending on its source, gelatin can be divided into two types; Type A, from acidic hydrolysis of animal skin, and Type B, from basic hydrolysis of bovine bones.
- Plasticizer: (E.g., Glycerin & Sorbitol) Plasticizers are added to polymers used as film-forming agents to make them pliable and soft, thereby enhancing the flexibility and plasticity of the films.
- Solvent: (E.g., Water) Water is used as a solvent in capsules.
- Opacifiers: (E.g., Titanium Dioxide) Opacifiers provide protection against light and photodegradation. They also play a role in concealing the capsules’ inner fill contents.
- Preservatives: (E.g., Antioxidant, Antimicrobial & Chelating Agents) These agents play a role in the preservation of capsule contents, which increase their shelf life and make capsules safe for consumption.
- Flavorings: (E.g., Essential oils, Sucrose, etc.) Flavoring agents are used to achieve taste masking in pharmaceutical dosage forms (capsules, hormonal tablets, etc.) to make them more suitable and acceptable for ingestion.
- Colorants: (E.g., Dye, Lakes, Mineral Colors, etc.) Coloring agents can impart various colors to capsule dosage forms. Colorants play an important role in improving patient compliance and can be further selected to complement the disease being treated.
What are the steps involved in manufacturing hormonal capsules?
Hard Gelatin Capsules
Hard gelatin capsules are a modern, solid dosage form for medicinal use, stemming from the increased emphasis on pharmacokinetics found in drug development today. This has considerably expanded the range of possible formulations utilizing hard gelatin capsules as a simple solid oral dosage form for drug delivery.
Formulation & Manufacturing of Empty Hard Gelatin Capsules:
- Preparation of Gelatin Solution: Creating a dipping solution for the two-piece capsule machines.
- Dip Coating: Applying the solution onto metal pins to simultaneously form the caps and the bodies.
- Rotation: Rotating the dip-coated pins to distribute gelatin over the pins uniformly.
- Drying: Removing water and solidifying the hard gelatin capsule shells.
- Stripping & Trimming: Removing excess material and shaping the capsules.
- Joining: Assembling the trimmed capsule shells, after which the capsules are ejected from the two-piece capsule machine.
- Polishing & Printing: Final touches to ensure the capsules are ready for use.
Filled Hard Gelatin Capsules:
- Inner Fill Formulation: Developing and preparing the inner fill formulation containing synthetic hormones as active pharmaceutical ingredients (or cytotoxic and high potency hormones) along with other formulation additives.
- Filling: Filling hard capsule shells via manual, semi-automatic, or automatic filling devices.
- Sealing: Sealing the dry-filled capsules.
- Cleaning & Polishing: Ensuring the capsules are clean and polished for final use.
Softgels
Soft-gelatin capsule technology enables the production of unit dose solid dosage forms referred to as soft gelatin capsules. Various contract service providers (CDMO & CMO) enable outsourcing the use of soft-gelatin capsule technologies for various non-sterile dosage forms and solid oral dosage form applications to bring superior compounds to market faster. They may have capabilities for contract manufacturing of steroid capsules and contract manufacturing for hormonal capsules.
Formulation & Manufacturing of Soft Gelatin Capsule:
- Raw Material Storage & Selection: Ensuring the quality and selection of raw materials.
- Weighing Ingredients: Measuring the ingredients for both inner and outer fills.
- Preparation: Preparing the inner fill material and soft shells.
- Encapsulation: Combining the prepared materials into soft gelatin capsules.
Process of Encapsulation:
- Transporting Materials: Moving the prepared inner fill and outer fill materials containing hormonal preparations or cytotoxic and high potency hormone drugs to encapsulation bays.
- Segregation: Each encapsulation capsule manufacturing machine is segregated into individual bays.
- Molten Gel: Pumping molten gel into the machines.
- Forming Ribbons: Creating two thin ribbons of gel on either side of the soft gel manufacturing encapsulation machines.
- Rolling & Sizing: Passing the ribbons over a series of rollers and dies to determine the size of the capsules.
- Inspection: Inspecting the softgel dosage forms.
- Packaging: Packaging the soft shell capsules.
- Storage & Distribution: Storing and distributing the finished product.
These steps ensure that hormonal capsules are manufactured to the highest standards, providing effective and safe treatment options for various hormonal imbalances and conditions.
During the formulation and manufacturing of solid dosage forms like capsules, the medicinal concoctions are carefully filled into the body of the empty capsules. This is done before the cap is pushed into place for hard gelatin capsules, or before the inner fill materials are selected for soft gelatin capsules to achieve the desired therapeutic effects.
Contract manufacturing of hormonal capsules involves using hormonal active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) as the inner fill materials. This applies to both soft gel and hard gel dosage forms, ensuring that the final product meets the specific therapeutic needs and maintains high standards of quality and efficacy. This meticulous process helps in delivering effective treatments for various hormonal imbalances and conditions.
Related Services





FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Semi-Solids & Gels
Semi-solid dosage forms include creams, ointments, gels, and pastes, designed for external application to the skin or mucous membranes. They are characterized by their thick consistency, which allows them to adhere to the application site for effective drug delivery. These dosage forms are used to treat a wide range of conditions, from skin diseases to localized pain relief.
Semi-solid dosage forms offer several benefits, including targeted drug delivery to specific areas, reduced systemic side effects, and enhanced patient compliance due to ease of application. They can provide both local and systemic effects, depending on the formulation, and are particularly useful for delivering drugs that are not suitable for oral administration due to stability or bioavailability issues.
The formulation of semi-solid dosage forms involves the selection of appropriate base materials (such as hydrocarbons for ointments, water or alcohol for gels, and various emulsifiers for creams) that determine the product's texture, stability, and drug release characteristics. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are then incorporated into the base, along with other excipients like preservatives, antioxidants, and skin conditioners, to achieve the desired therapeutic effect and product stability.
Stability considerations for semi-solid dosage forms include maintaining the consistency, efficacy, and integrity of the product throughout its shelf life. This involves ensuring the physical stability (to prevent separation or crystallization of components), chemical stability (to prevent degradation of active ingredients), and microbiological stability (to prevent contamination). Stability testing under various conditions is critical to determining the product's expiration date.
Ensuring uniformity of dosage in semi-solid forms involves rigorous manufacturing processes and quality control measures. The manufacturing process must ensure thorough mixing and homogenization of the API throughout the base. Quality control tests, including content uniformity and viscosity measurements, are conducted on each batch to ensure that the final product meets the specified criteria for uniformity and consistency.
Yes, semi-solid dosage forms can be designed for controlled release of the active ingredient. This is achieved through the use of specific formulation strategies and excipients that modify the drug release profile, such as polymers that form a matrix with the drug or encapsulation techniques that slow the diffusion of the drug from the base. Controlled release formulations can enhance therapeutic efficacy and improve patient compliance by reducing the frequency of application.
Packaging options for semi-solid dosage forms include tubes, jars, pump dispensers, and single-use sachets. The choice of packaging is based on the product's viscosity, intended use, and stability requirements. Packaging materials must protect the product from contamination, light, and air, and be compatible with the formulation to prevent interaction with the packaging.
Quality assurance testing for semi-solid dosage forms includes physical, chemical, and microbiological tests. Physical tests evaluate the product's appearance, pH, viscosity, and spreadability. Chemical tests assess the potency and purity of the active ingredients and the presence of degradation products. Microbiological tests ensure the product is free from harmful microorganisms. All tests are conducted in accordance with regulatory guidelines to ensure product safety and efficacy.
c
Regulatory considerations for semi-solid dosage forms involve compliance with guidelines provided by regulatory agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and others. These guidelines cover the formulation, manufacturing process, quality control, packaging, labeling, and stability testing. The submission of a New Drug Application (NDA) or Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) is required for market approval, including detailed documentation of the product's formulation, manufacturing process, and validation of analytical methods.
Hycon Labs offers comprehensive services for the development and manufacturing of semi-solid dosage forms, including formulation development, process optimization, scale-up, manufacturing, and packaging. Hycon can provide expertise in selecting appropriate base materials, excipients, and manufacturing processes to meet the product's specifications and regulatory requirements. Additionally, Hycon can assist with stability studies, quality assurance testing, and regulatory submission, facilitating a smooth path from concept to commercialization.